Magic mushrooms, also known as psilocybin mushrooms or “shrooms,” have been used for centuries in various cultural and spiritual practices. Today, there is a resurgence in interest surrounding their potential for treating mental health disorders through psilocybin-assisted therapy.
In this article, we’ll dive deep into the world of magic mushrooms, exploring their history, the science behind their effects, and the promising applications in therapy.
Stay with us as we take you on a journey to unlock the healing potential of these fascinating fungi.
Understanding Psilocybin Mushrooms
Definition and Main Types
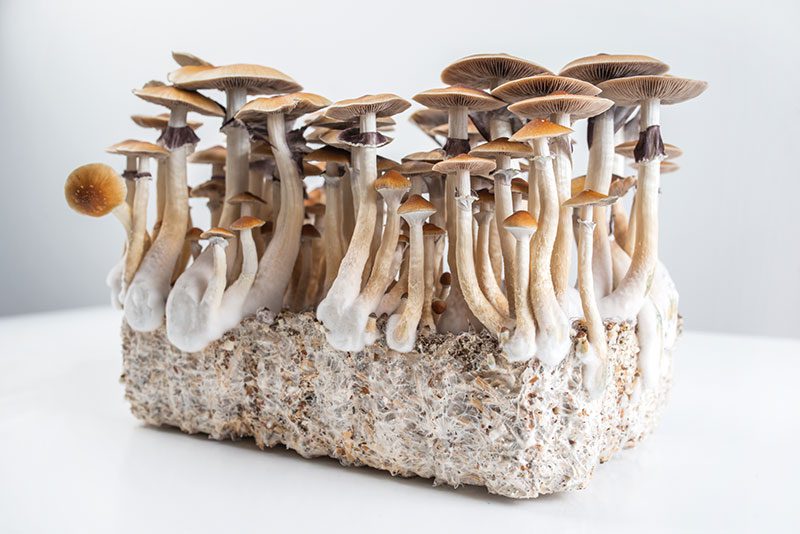
Psilocybin mushrooms, commonly known as magic mushrooms or shrooms, are a group of fungi containing psychoactive compounds. These compounds induce altered states of consciousness and can produce a range of sensory, emotional, and cognitive effects.
There are over 200 species of psilocybin mushrooms, but the most well-known and widely used is Psilocybe cubensis. This species is often cultivated for recreational and therapeutic purposes due to its potency and ease of growth.
Active Compounds: Psilocybin and Psilocin
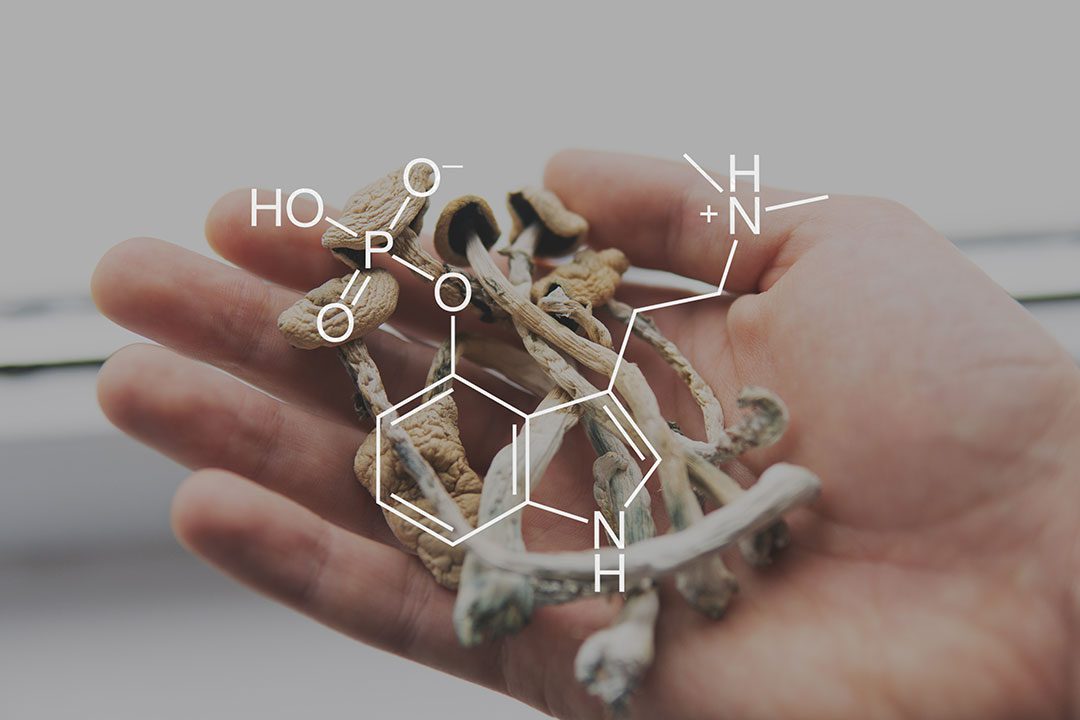
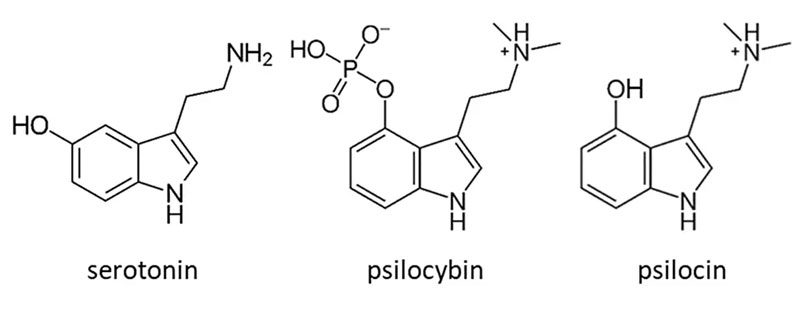
The primary psychoactive compounds found in magic mushrooms are psilocybin and its active metabolite, psilocin. When ingested, psilocybin is broken down into psilocin, which then interacts with the brain to produce its effects.
It’s important to note that different species of mushrooms can contain varying levels of psilocybin and psilocin, which can lead to differences in their potency and effects.
Effects and Experiences
The effects of magic mushrooms can vary depending on factors such as the dose, individual sensitivity, and the specific mushroom species consumed. However, some common experiences include:
- Visual and auditory hallucinations
- Altered perceptions of time and space
- Enhanced emotions and feelings of connectedness
- Spiritual or mystical experiences
While many users report positive experiences, it’s important to recognize that some may experience adverse reactions such as anxiety, paranoia, or panic. These “bad trips” can be influenced by factors like an individual’s mindset and the environment in which the mushrooms are consumed.
In the context of therapy, the experiences induced by psilocybin mushrooms can help individuals gain insights, confront difficult emotions, and foster personal growth.
The Science Behind Magic Mushrooms and Mental Health
The Role of Serotonin in the Brain
Serotonin is a neurotransmitter that plays a crucial role in regulating various brain functions, including mood, appetite, sleep, and cognitive processes. Imbalances in serotonin levels have been linked to several mental health disorders, such as depression, anxiety, and PTSD.
Many conventional treatments for these conditions, like selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), aim to increase serotonin levels in the brain. However, they are not always effective and can come with undesirable side effects.
How Psilocybin Interacts with Serotonin Receptors
Psilocybin’s active metabolite, psilocin, has a similar structure to serotonin, allowing it to bind to and activate certain serotonin receptors in the brain. This interaction, particularly at the 5-HT2A receptor, is believed to play a significant role in the psychedelic effects and therapeutic potential of magic mushrooms.
By activating these receptors, psilocybin mushrooms can induce changes in brain activity, connectivity, and neuroplasticity. These alterations can lead to shifts in perception, mood, and cognition, which can be harnessed for therapeutic purposes.
Recent studies have shown that a single dose of psilocybin can produce lasting improvements in mood and well-being in individuals with treatment-resistant depression. Additionally, psilocybin has demonstrated promise in reducing anxiety and depression in patients with life-threatening illnesses.
In essence, the interaction between psilocybin and the brain’s serotonin system can facilitate profound experiences that may promote healing and personal growth in those struggling with mental health issues.
Promising Areas of Psilocybin-Assisted Therapy
As research on psilocybin mushrooms continues to grow, several areas have emerged as particularly promising for their therapeutic potential. Here, we will discuss some of the key applications currently being explored.
Treatment-Resistant Depression
Depression is a pervasive mental health disorder, and conventional treatments are not effective for everyone. Treatment-resistant depression refers to cases where individuals do not respond to multiple attempts at treatment, leaving them struggling with debilitating symptoms.
Psilocybin-assisted therapy has shown promise in helping those with treatment-resistant depression by providing rapid and sustained improvements in mood. Clinical trials have demonstrated that a single high-dose session can lead to significant reductions in depressive symptoms that persist for weeks or even months.
Anxiety Disorders
Anxiety disorders are among the most common mental health conditions, and they can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life. Psilocybin has demonstrated potential in reducing anxiety symptoms and improving overall well-being.
Studies have found that psilocybin-assisted therapy can help reduce anxiety and depression in individuals with life-threatening illnesses, such as cancer. These improvements have been found to persist for months after treatment, suggesting that psilocybin may offer a valuable tool for managing anxiety disorders.
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder
Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is a debilitating condition that can result from exposure to traumatic events. Psilocybin’s ability to promote neuroplasticity and induce transformative experiences has led researchers to explore its potential as a treatment for PTSD.
While research on psilocybin for PTSD is still in its early stages, preliminary findings are encouraging, suggesting that psychedelic-assisted therapy may help individuals process and integrate traumatic memories, leading to symptom reduction.
Substance Use Disorders
Psilocybin mushrooms may also have potential in treating substance use disorders, such as alcohol and nicotine addiction. Research has shown that psilocybin-assisted therapy can lead to significant reductions in substance use and cravings.
By facilitating introspection and promoting lasting shifts in perspective, psilocybin may help individuals overcome the underlying emotional and psychological factors driving their addiction, ultimately supporting long-term recovery.
These are just a few examples of the promising applications of psilocybin-assisted therapy. As research advances, we may continue to uncover new ways in which magic mushrooms can support mental health and well-being.
Microdosing: A Different Approach to Psilocybin Therapy
Definition and Rationale Behind Microdosing
Microdosing is the practice of consuming sub-perceptual doses of psychedelic substances, such as psilocybin mushrooms, on a regular schedule. These doses are typically around 1/10th to 1/20th of a typical recreational dose, and the intention is to experience subtle cognitive and emotional enhancements without the intense hallucinogenic effects.
The rationale behind microdosing is that these small doses may still provide therapeutic benefits, such as increased creativity, focus, and emotional resilience, without the need for a full-blown psychedelic experience.
Potential Benefits and Applications
Proponents of microdosing claim that it can lead to a variety of benefits, including:
- Improved mood and emotional stability
- Enhanced cognitive function and creativity
- Increased energy and motivation
- Reduced anxiety and depression
Microdosing may also offer a more accessible and manageable approach to psilocybin therapy for those who are hesitant or unable to participate in high-dose psychedelic experiences.
Current Research and Anecdotal Evidence
While there is a growing body of anecdotal evidence supporting the benefits of microdosing, scientific research in this area is still in its infancy. Preliminary studies have suggested that microdosing may improve cognitive flexibility, creativity, and emotional well-being. However, more rigorous research is needed to confirm these findings and establish the safety and efficacy of microdosing as a therapeutic intervention.
Despite the lack of conclusive evidence, the interest in microdosing continues to grow, and it has the potential to become an important area of psychedelic-assisted therapy. As research advances, we may gain a better understanding of the benefits, risks, and best practices associated with this unique approach to psilocybin therapy.
Challenges and Future Directions
While the potential of psilocybin mushrooms for mental health treatment is promising, there are several challenges and obstacles to overcome before they can be fully integrated into mainstream therapy. Here, we will discuss some of these challenges and consider possible future directions.
Overcoming Stigma
The stigma surrounding psychedelics, including magic mushrooms, has hindered research and acceptance for decades. Changing public perception and dismantling the negative stereotypes associated with these substances is a crucial step towards their broader acceptance in mental health treatment.
Efforts to educate the public and healthcare professionals about the therapeutic potential of psilocybin and other psychedelics can help challenge misconceptions and foster a more open-minded approach to these powerful tools.
Ensuring Safety and Standardized Protocols
As with any therapeutic intervention, ensuring the safety of patients is of utmost importance. Developing standardized protocols for psilocybin-assisted therapy, including proper dosing, set and setting, and the integration of psychological support, is essential to minimize risks and maximize benefits.
Further research is needed to better understand the potential risks and contraindications associated with psilocybin therapy, as well as to establish best practices for different populations and clinical contexts.
Scaling Up Psychedelic-Assisted Therapy
The current model of psychedelic-assisted therapy often involves resource-intensive protocols, such as hours-long therapy sessions and the need for trained facilitators. Scaling up these interventions to reach a broader population will require innovative solutions and adaptations to traditional therapeutic models.
For example, developing group therapy models, teletherapy options, or integrating psilocybin therapy with existing mental health services may help increase accessibility and reduce costs.
Final Thoughts on Psilocybin-Assisted Therapy
The potential of psilocybin mushrooms for mental health treatment is vast, and ongoing research continues to uncover new applications and insights. By addressing the challenges and obstacles that stand in the way, we can work towards responsibly integrating these powerful tools into mainstream mental health care, potentially transforming the lives of countless individuals struggling with mental health issues.